Do you want to know what’s the difference between WordPress Pages vs Posts?
If you’re thinking of adding new content to your WordPress site, then it’s essential to know which type of content to add. Pages and Posts are the two primary forms of content supported by WordPress and it’s important to learn when to use each.
Both of these options might seem alike as both are associated with website content and are available on the top left side of the WordPress Dashboard. However, they differ in various technical details.
In this article, you’ll get a brief knowledge of WordPress Pages vs Posts. We will tell you all about their proper use so that you’ll know how to best use them on your website.
A) What Are Pages in WordPress? – Introduction
Let’s start with the basics. Pages simply refer to the content that doesn’t change often, known as static content. It includes content like ‘About Us’, ‘Contact Page’, ‘Services’, ‘Privacy Policy’, and others. Sometimes even your homepage can count as static content. As they are static, pages rarely need updates and are timeless entities.
For example, we can take the ‘About Us’ or ‘Contact Us’ pages of ThemeGrill. The ‘About us’ section provides a brief introduction about the company. Similarly, the ‘Contact Us’ page provides contact details to the users wishing to connect.
As you can see, Pages store important pieces of information for your audience. They don’t require frequent changes as that information will remain forever on your website once updated.
There are some typical features of Pages in WordPress. The first one is that you can’t mention information like dates, time, or authors in your pages. Even though WordPress stores them in its database, it won’t appear on the screen. Pages also don’t have comment sections since they aren’t meant to be social or open to discussion.
Now, after a brief introduction to WordPress Pages and its features, let’s look at the part on when to use it.
When to Use Pages in WordPress?
Pages are static entities, so they contain primary information without which the website might look incomplete. Thus, you can use site pages to let your audience know about who you are, what you do, and what you offer. Being permanent content, their advantage is that you only have to write and post them once.
Pages can also express core ideas about your business that doesn’t need to be changed often, such as ‘Services’, and ‘About Us’. If those pages are well done, it can even help generate some loyal audience towards your site.
Likewise, you can also use pages for creating some attractive gallery pages or landing pages (a page where your audience lands after clicking into certain links or Google ads). All thanks to the custom page templates which we will discuss in detail later.
How Can You Create Pages in WordPress?
Creating the static content on your website like the ‘About Us’ or ‘Contact Us’ is no longer a difficult task. Just follow the following step by step guidelines and you are good to go:
First, log in to your WordPress Admin area by typing in your WordPress login URL. For example, if your website is https://www.example.com, you’ll need to go to https://www.example.com/wp-login.php.
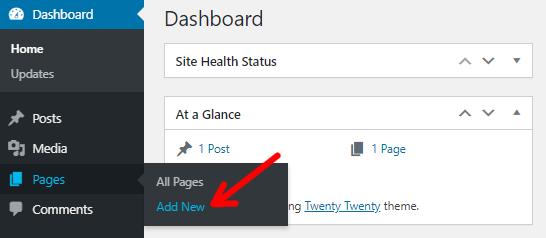
After logging in, go to the ‘Pages’ option available on the left-hand menu. Click ‘Add New’ to create a new page. You can also click on ‘All Pages’ and create a new page from there.
After that, you’ll enter the WordPress Page Editor where you can add content for your page. For example, you can make an about page for your site.
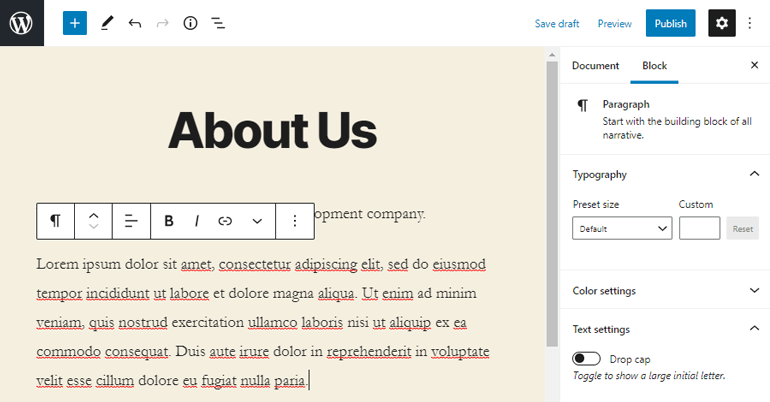
Once your content is ready, click on the ‘Publish’ button on the top right corner of the editor.
B) What Are Posts in WordPress? – Introduction
Now let’s dive into Posts. Posts or Blog Posts are blog entries or articles that are constantly updated. They are the dynamic type of content that appears on the feed. It can include writings like news/articles, reviews, stories, journals, etc. This piece of content includes informational updates about certai
n topics or discussions.
WordPress Posts are appropriate for blogging, trending news, articles, announcements, or just content relating to a certain niche. The best example of Posts is the one you are reading right now on this site; a brief discussion on WordPress Pages vs Posts.
Another example of Posts is the blog section of ThemeGrill which presents you with the list of articles on various topics related to WordPress.
In almost every Post, there is information about the author and its published dates. Contrary to Pages, updates about time, date, and author’s info are visible for Posts. These are also important as Posts are arranged by date in reverse chronological order. It means the latest content will appear on the topmost side of the site.
Moreover, there are features like comment sections and social sharing options in Posts. It makes your site connected to the audience and gets their feedback. Regarding the arrangement of posts, you can use Categories and Tags. They can help you classify your posts into different sections.
When to Use Posts in WordPress?
Posts in WordPress can help you say or convey something to the audience. This information relates to the type of your website and focuses more on generating leads. Thus, the content for posts includes the latest news and fresh knowledge that would interest readers.
In most cases, Posts are best for blogs, news articles, stories, events, announcements, and other niches that need frequent content updates.
Similarly, subject matter like ‘How to’, ‘Why’, and several FAQ articles are best explained using posts. Likewise, given their dynamic nature, Posts are also for things that involve open discussion amongst the audience.
Thus, if you have a blogging site or site where you publish content regularly, you will use posts for the majority of your website’s content.
How Can You Publish/Add WordPress Posts?
There are several ways to make your posts appear on your website. Go through the following steps to start to get started with WordPress Posts:
First, log in to your WordPress Admin area by going to your login WordPress login URL. For example, the login URL looks like this: http://www.example.com/wp-login.php (Replace http://www.example.com with your website URL.)
After logging in, go to the ‘Posts’ option available on the left-hand menu. Click on the ‘Add New’ link and you’ll see the ‘Add New Post’ where you can create your first post. Likewise, you can do the same after clicking the ‘All Pages’ options too.
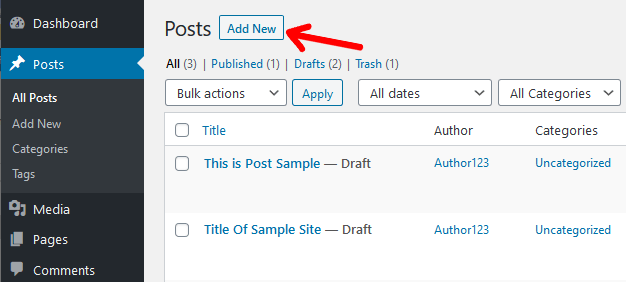
Afterward, the WordPress Post Editor opens up where you can add various types of content. For example, you can create blogs, articles, news, etc for your site.
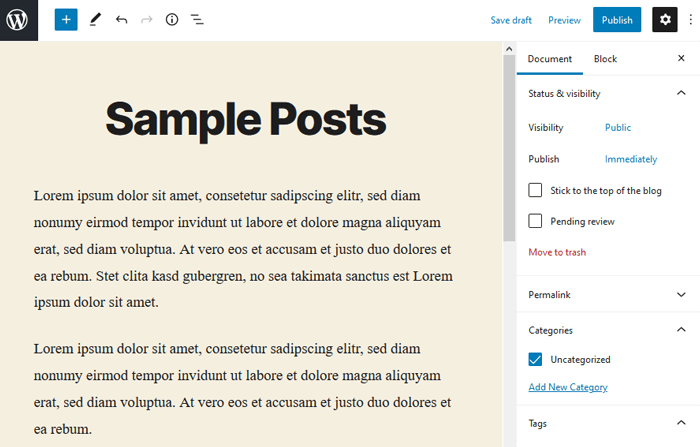
Finish the article with a proper title and after its completion, click on the ‘Publish’ box at the top right column on the screen
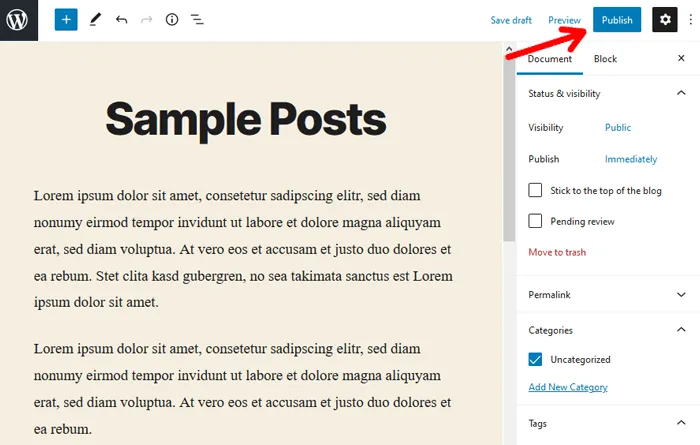
Before publishing, you can preview your posts through the ‘Preview’ button. It is right beside the ‘Publish’ option. Likewise, there’s the section of categories and tags through which you can organize your WP Posts.
C) Key Differences Between WordPress Pages & Posts (Explained)
Now let’s move along with the brief explanation of the major differences between WordPress Pages vs Posts:
1. Basic Definition
From their basic definition, Pages tend to be static while Posts are dynamic on a website. Posts usually have timely updates as they contain the content on trending subject matter or discussions. But the content of the page is timeless as it publishes static information that will be relevant on your website for a very long time.
Common examples for Pages are ‘About Page’, ‘Contact Us Page’ along with Company Policies and Services. Whereas, Posts include sections like blogs, stories, trending news/articles.
Pages are typically listed in the site’s primary navigation menu at the top of the site. While Posts are linked to the menu system.
2. Details About Published Date, Time, and Author
It is one of the major differences between WordPress Pages and Posts. Pages don’t include the information on published date, time, and authors. It’s because of its static and timeless nature. The information might be saved on the WordPress database but it’s not public.

Being the dynamic content, Posts include information like published dates and the author’s details. The mentioned dates help manage the Posts on your site since the newest Posts appear at the top while the oldest ones are at the bottom.
Alongside this, you can also have clickable links to the author’s profile where you can browse the list of all articles published by the author.
3. Attributes and Arrangements
Knowing how to arrange the content on your website is not just important but essential. There are various options with which you can arrange different types of content in Pages and Posts.
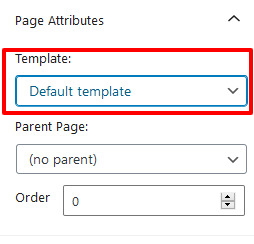
As we know, pages don’t include time and date, categories, or tags, so it has different options for their arrangement. Instead, it features a hierarchical arrangement where you can create subpages or child pages for every individual/parent page.
It’s an easy way in pages to arrange the related content of your website together. For this, you need to choose a Page to become the Parent Page and then create its subpages through the ‘Page Attribute’ section in the lowermost right menu.
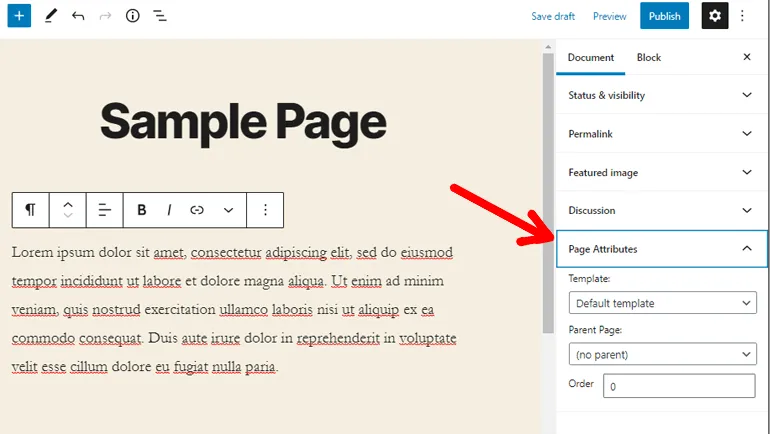
However, this type of arrangement in Pages affects the URL permalink structure of subpages. If the URL for the parent page is ‘example.com/parent’, then that of the child page would be ‘example.com/parent/child’.
On the other hand, you get the option to assign categories and tags when you create WordPress Posts. The options are available on the right side of your screen.
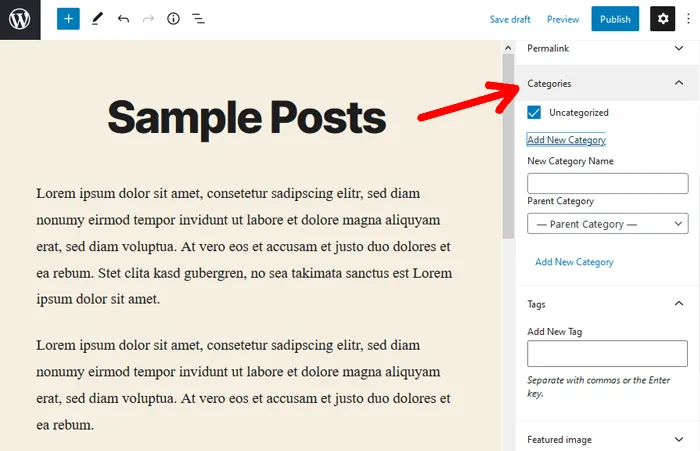
Each category and tag archive assigns a typical section or keywords to a bunch of posts. This idea helps to organize posts systematically and ease readers into the related content that interests them. Instead of giving them a particular category or tag, you can also arrange them simply by their published dates.
For example, look at the blog section of ThemeGrill. The Posts there are arranged by their published dates and also through categories like:
- Beginner’s Guide
- Plugins Collection
- Themes Collection
- Comparison
- SEO
- Tips & Tutorials
- Reviews, etc.
3. Syndication on RSS Feed
Real Simple Syndication (RSS) is a platform that connects websites or blogs with their audience. It lets readers keep track of any updates from their preferred websites. For a site to appear in the RSS, the website owner should include it as a subscription option while readers must subscribe to that site.
For bloggers, they can use the RSS feeds for delivering the updates via Feedly, Mailchimp, Aweber, or Constant Contact. While for readers, all they have to do is subscribe and sign up. Whenever the website owner/author updates content on their site, the subscribers are instantly notified. This way, the readers won’t miss anything.

Since there are rare to no updates in Pages, they aren’t going to appear in the RSS feeds. Posts, on the other hand, are dynamic and information about time and date matters here. They are updated regularly so it becomes necessary to notify readers about the updates. As a result, Posts appear in blog posts listing and are syndicated in RSS feeds.
4. Comment Section and Social Feature
Analyzing all of their properties, we can conclude that Pages aren’t social. They have neither a comment section nor social sharing buttons. Thus, there is no way to connect with your audience directly through pages. This makes quite a lot of sense as you don’t want public comments on your company policies or contact page.
In the WordPress page editor, there’s ‘Discussion’ option on the right column which includes ‘Allow Comments’ option. But it’s disabled by default. And rarely any site would enable this.
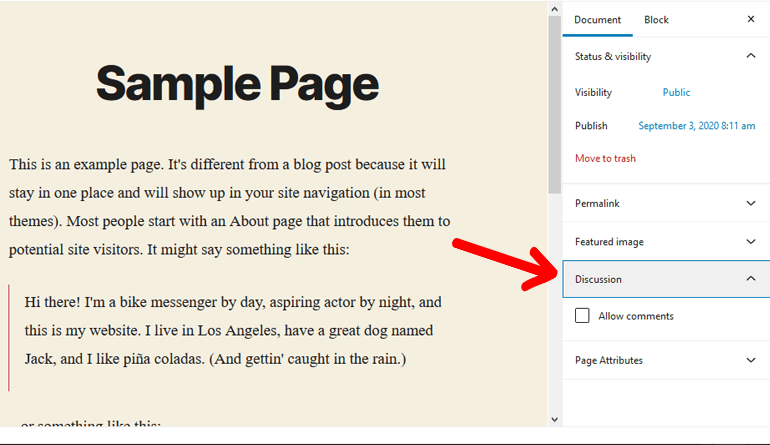
On the other hand, WordPress posts most often have this option enabled by default. Therefore through the comment section in your post articles, you can engage and interact with your website audience.
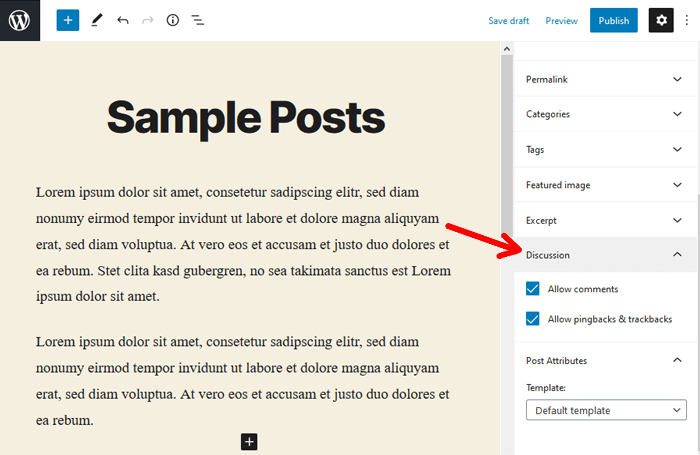
With the available social sharing plugins, you can add a social sharing option to your posts. Using the social sharing buttons, your users can share your website articles on their social media profiles and various online groups.
Hence, posts are largely used for social media marketing strategies.
5. Content Layout
WordPress Posts have a custom format or ‘Post Formats’. This customization enables you to style the article depending on the type of content. You have the option to stylize for images, videos, qu
otes, gallery, etc.
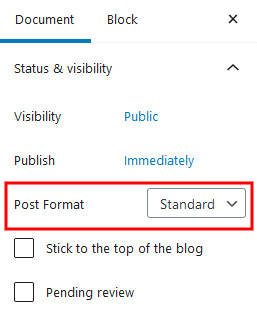
In addition to the default options, you may sometimes find more types of post formats. Such may be added by WordPress themes and plugins as well.
Pages don’t have such a content layout. Rather they have ‘Page Templates’. This feature allows you to use different layouts on different pages. Even you can create your templates for pages & subpages (child pages). However, this task might not be as easy as it sounds. You may need some technical assistance to perform this task.
D) Are There Any Similarities Between WordPress Posts and Pages?
Despite these differences, Posts and Pages have some similarities too. Here, we’ve enlisted some of the major similarities between pages and posts.
- Both of them belong to WordPress and they help in creating and publishing content.
- The editor for both WordPress pages and posts look alike and also work in a similar way. In fact, it’s the same editor; the block-based Gutenberg editor. However, there will be some differences in the document settings, like comments, categories or page attributes, etc. as discussed above.
- As it’s the same editor, the content elements you can add to posts and pages are also the same. You can add text, images, gallery, forms, etc.
Despite the differences and similarities, both pages and posts are useful for a full-fledged website. Now that you know when to use each one, we hope you can create a professional WordPress website with the right forms of content.
E) Frequently Asked Questions on “WordPress Pages vs Posts”
Now after the brief discussion on WordPress Pages vs Posts, here are some FAQs related to it.
1. Is there any limitation on creating Posts or Pages in WordPress?
No, there is no such limit. You can create any number of posts or pages you need.
2. Should I use Pages or Posts?
Both forms of content have their respective roles and are important in WordPress sites so it depends on the type of content. For content that needs a rare change like ‘Contact Us’ or a list of services, use Pages. For blogs, journals, stories, or articles, you can go for Posts.
3. Between Pages and Posts, Which is Better for SEO?
Both WordPress posts and pages have SEO settings capable enough to rank on search engine result pages. However, since posts are mostly used for dynamic and timely content, they’re produced more. As a result, they’re more likely to appear on the search results.
Besides that, the quality of your content plays a vital role in your site’s ranking. As long as your content maintains its quality, both Posts or Pages can get a good ranking on search results.
4. Can both Blog Posts and Site Pages in WordPress work Side by Side?
Of course. WordPress enables you to use a combination of Site Pages and Blog Posts. It’s a good idea to include a combination of both on your site. However, you can omit either of them as well, based on your site’s purpose.
5. Can I convert Posts to Pages in WordPress and vice-versa?
Sometimes you can create Posts instead of Pages by mistake. You can solve this situation with ease. All you need to do is move the content over to the place you wanted.
Follow this step by step process for converting posts to pages:
- Click on the ellipses (…) which would in the top right corner in the respective page/post editor
- Then, click ‘Copy All Content’ which is on the lowermost left
- Open a new tab in your browser and create a new page/post that you wanted
- In the new page/post, click on the ellipses (…) once again and select ‘Code Editor’
- Paste the copied content in the blank space
- Exit the Code Editor
6. How does the RSS Feed work for Posts?
RSS feeds of any website or podcast maintains new updates or notifications. You can either check this list on your own, or you can subscribe to the feed so updates will show up. Thus, RSS feed works for posts by informing your readers about the new posts on your site.
7. Are Posts and Pages the Only Content You Can Create on WordPress?
No, there is another option of content known as Custom Post Types or CPT. However, it’s not an easy task as it needs plugins and third-party WordPress themes. The most common examples of CPT are portfolio projects, real estate listings, and testimonials.
Conclusion
To wrap up, there are basic as well as various technical differences between WordPress pages vs posts. Pages in WordPress are the static content that includes information that doesn’t need to be updated. In contrast, Posts in WordPress are dynamic content like blogs, articles, news, and stories.
Thus, if your website demands static content, you should go with WordPress Pages. Likewise, if your website needs dynamic content and regular interaction with the audience, there is no better option than WordPress Posts. However, most websites include both forms of content.
So, this was the explanation of the major differences between WordPress Pages vs Posts. Hope you all found it helpful. And now after you’ve gained knowledge regarding their importance and usage, we hope you can utilize them to improve your website.
If this article made you want to know more about WordPress, you can check our article ‘Everything You Need to Know About WordPress’.
If you found it useful, please don’t forget to share the article on your social media networks. And, leave a comment if there’s any feedback or suggestion for us.
The post WordPress Pages vs Posts – What’s the Difference? (Explained) appeared first on ThemeGrill Blog.