Key takeaways
In this article…
What is an HRIS?
Human resources information systems (HRIS) are centralized repositories for employee data. One of the benefits of HRIS is that they are designed to help HR teams streamline and automate a variety of functions ranging from basic human resources (HR) tasks like payroll to more nuanced processes like performance management.
In some cases, an HRIS consists of multiple subsystems that work together to create a holistic view of an organization’s workforce. In other cases, an HRIS is a specialized, standalone tool that drills into one or two subsystems.
Learn more in our video overview:
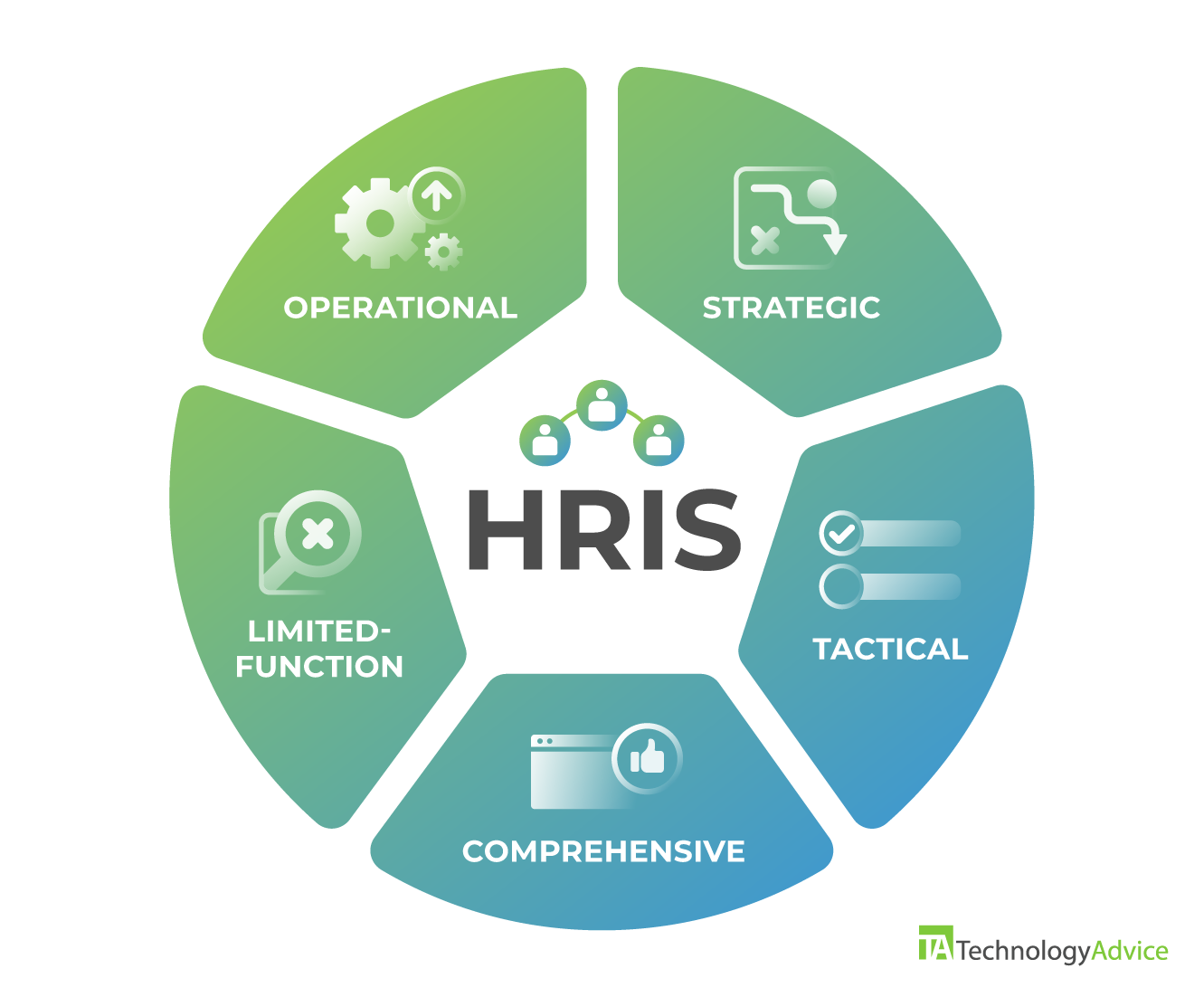
5 types of HRIS and their use cases
All HR information systems fall into five main types based on function or scope:
- Operational HRIS
- Strategic HRIS
- Tactical HRIS
- Comprehensive HRIS
- Limited-function/specialized HRIS
Both limited-function and comprehensive HRIS solutions may house different quantities and types of data that fall across the three different functional types of information systems.
1. Operational HRIS
The operational HRIS category includes tools that assist HR staff and people managers with hiring, promotions, transfers, and other talent management needs. Operational HRIS solutions focus on improving existing systems by making them more efficient and impactful.
Applicant tracking system (ATS)
An applicant tracking system (ATS) logs all open positions within an organization and optimizes workflows to fill them as quickly as possible. ATS functions include syndicating job postings to multiple job boards, screening applications to identify qualified candidates, and identifying bottlenecks within the hiring process.
Example
Workable automates tasks like publishing job posts, sorting applicant résumés, and scheduling interviews. Automating these tasks helps streamline the screening and recruitment process, increases efficiency, and reduces the chances of human error.
Performance management system
A performance management system stores employee information regarding performance appraisals. It supports employee retention, promotion, transfer, job rotation, contract termination needs, and other talent management concerns. A performance management system helps managers take action if an employee is under-utilized or needs extra support.
Example
An integral part of a performance management system is conducting regular performance reviews to identify employee strengths and areas of opportunity. To help streamline this process, Leapsome automates review cycles and allows employees to set and track personal and organizational goals.
The performance appraisal feature collects and provides the data and documentation necessary to make critical decisions regarding employee retention. This includes deciding whether to retain, promote, transfer, or terminate an employee.
2. Strategic HRIS
Modules and functions within strategic HRIS systems help with analysis, decision-making, and goal-setting in relation to human capital management. Strategic HRIS solutions often help companies plan for growth and expansion by finding and retaining the right talent.
Workforce planning
Workforce planning tools help HR teams identify the necessary background and skills, responsibilities, reporting structure, and salary for any given role. This functionality helps develop strategies for filling skills and role gaps in the current workforce, which has downstream implications for recruiting strategies as well as learning and development plans.
Example
Rippling’s headcount planning creates approval workflows and helps you budget for current and future employees. This gives you a quick view of the actual headcount and allows you to compare it against the planned headcount. You can also view the number of headcount in each phase of the hiring process, as well as the range of total compensation and annual bonus.
Rippling’s headcount planning module aids in planning for company growth and expansion by clarifying the costs related to necessary positions. Understanding these data allows for effective budgeting for crucial roles.

Learning management system
A learning management system (LMS) supports succession planning as operational decisions are made regarding job rotations or promotions. It tracks skill sets for employees across the company and identifies employees who are ready to pursue additional training or certifications based on recent changes to their roles or responsibilities.
Example
360Learning helps you create a course that supports different content types, incorporates gamification elements to increase user engagement, and allows managers track learners’ progress. These features significantly enhance learning management within a strategic HRIS because they align employee development with company goals and prepare them for future company needs.

3. Tactical HRIS
The tactical HRIS category targets efficiency and compliance for internal workforce management. The tools and functionalities that fall in this category help HR leaders make decisions on how to best use existing resources for functions such as compensation, recruiting, training, and benefits.
External data aggregation
Tactical human resource modules aggregate external data related to a business’s competitors, industry, and compliance requirements. This information provides benchmarks in areas such as talent acquisition, employee satisfaction, compensation, DEI, and performance management.
Example
Deel tracks compensation data across international markets to help determine whether a proposed payment rate is higher, lower, or on-par with similar roles in a specific geographic region.

Benefits administration system
Compensation and benefits management impact employee experience and are two of the largest business expenses. Company leaders have a vested interest in regularly reviewing the organization’s benefits package as part of an employee’s total compensation. If an HRIS indicates a particular benefit is being underutilized among employees, HR leaders may need to remind employees about the benefit or decide to invest in a different benefit instead.
Example
TriNet helps users identify how employees are utilizing company benefits. If you find that a benefit is not being utilized effectively, you can also use TriNet’s marketplace to compare benefits and find one that supports your employees’ specific needs.

4. Comprehensive HRIS
As the name implies, a comprehensive HR information system functions as a one-stop shop for storing any information needed to perform nearly all HR management functions. It serves as a central repository for a wider range of data that supports operational, strategic, and tactical HR functions combined.
These three functions don’t operate in a vacuum; rather, they influence each other in different ways. For example, information about where a role fits into the reporting structure and how it contributes to the company’s goals serves both operational and strategic angles of job analysis and design.
It makes sense for larger businesses to use a comprehensive HRIS since it consolidates data across all three types of functional systems. This information provides valuable insight so HR and business leaders can make informed decisions quickly.
Smaller businesses, on the other hand, may want a simpler HRIS platform that fulfills only core human resources management needs such as payroll. In this case, a comprehensive HRIS may be overwhelming to implement and maintain. The higher cost also puts all-in-one HR suites out of reach for many smaller businesses’ budgets.
Example
BambooHR is a popular all-in-one tool with HRIS key features to support onboarding, performance management, payroll, and benefits administration.

5. Limited-scope or specialized HRIS
In contrast to a comprehensive HRIS, a limited-function HRIS focuses on one or a few core information systems. They typically support a narrow list of HR functions, such as payroll and benefits administration and are a better investment for businesses’ with specific tactical needs that can’t be addressed by an all-in-one solution.
No matter what HR function(s) a company focuses on with a limited-function HRIS, an employee information system is essential to the HR software. This system collects, archives, and tracks personal and professional employee records, including name, address, minority status, citizenship, education, and past professional experiences.
Limited-function HRIS platforms are often less expensive compared to comprehensive HRIS solutions, and solo HR professionals can manage this kind of software alone. For these reasons, small companies with lean HR teams may find limited-function HRIS platforms more manageable.
Example
When I Work focuses on workforce management and is best for organizations that need to effectively schedule shifts. When I Work’s more advanced features, like automatic scheduling and labor costing, make it a better option for companies with primarily frontline workers compared to comprehensive HR without these specialized abilities.

How to choose the right type of HRIS
There are many HRIS solutions available that fit a wide range of needs, so the quest to find the best fit comes down to two questions:
Choose limited-scope HRIS if:
Choose comprehensive HRIS if:
Ultimately, the right type of HRIS depends on the unique needs your company faces now and in the future. Keep these needs top of mind as you explore our comprehensive list of solutions in our HR Software Guide.

About the author