
FreeBSD comes with different utilities, which can be used to gather the information as per your needs. The uname command is used to print system information, and dmesg command is used to print kernel ring buffer information. The sysctl command is use to configure kernel parameters at runtime as well as to read hardware information. Let us see all commands that can display hardware information on the FreeBSD server or desktop.
FreeBSD Display Information Hardware Using the CLI
Following list summaries, all the command you need to gather FreeBSD hardware information.
Determining the FreeBSD Hardware Type/platform
# uname -m
Find machine processor architecture:# uname -p
Determining FreeBSD release level:# uname -r
Generally, following command is use to get all info at a time:# uname -mrs
Sample outputs:
FreeBSD 5.0-RELEASE i386
One can find out if we are using 32 or 64 bit FreeBSD kernel/system:getconf LONG_BIT
How To Find Out FreeBSD Version and Patch Level Number
Run:freebsd-version
FreeBSD CPU info
Finding CPU information such as speed, make etc# dmesg | grep CPU
Sample outputs:
CPU: Pentium 4 (1716.41-MHz 686-class CPU) acpi_cpu0: on acpi0 acpi_cpu: CPU throttling enabled, 8 steps from 100% to 12.5%
One can filter out unwanted information using the grep command/egrep command;# dmesg | grep ^CPU
Another option is to type the following sysctl command:sysctl -a hw.model
sysctl -a | grep -i hw.*cpu
Getting info about the memory on FreeBSD
Getting real and available memory to FreeBSD box:# dmesg | grep memory
Output:
real memory = 201326592 (192 MB) avail memory = 188555264 (179 MB)
Alternatively, try following command to grab memory information on FreeBSD:# sysctl -a | grep hw.*mem
# sysctl -a | grep mem
Output:
hw.physmem: 194985984 hw.usermem: 167641088 hw.cbb.start_memory: 2281701376
Note systcl has more info, just type the sysctl command to see rest of all information:# sysctl -a | less
Please note that dmesg command information is retrieved on boot. After a while of server usage, that data can be “lost.” Therefore, I suggest that use grep command directly on /var/run/dmesg.boot file:
grep ^CPU /var/run/dmesg.boot grep -w 'memory' /var/run/dmesg.boot |
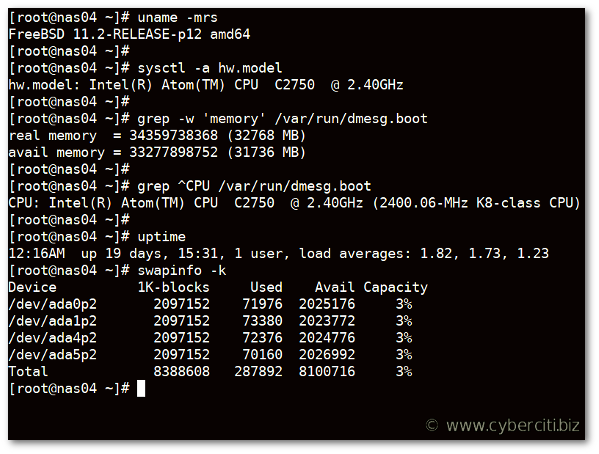
How to find out free and used memory size on FreeBSD
One can run either top command or htop command that displays the top processes on the system, including free and used memory:top
ORhtop ## need to install using 'pkg install htop' ##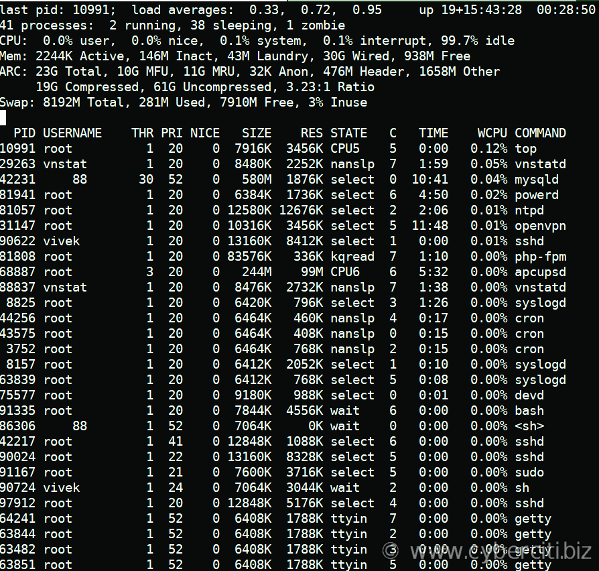
Another option is to install freecolor utility. It is a free replacement that displays free memory graphically as a bargraph. It supports the same options as free command from Linux:# pkg install freecolor
Run it:# freecolor -t -m -o
Determining how long a system has been up
# uptime
Finding out when a system was last rebooted or shutdown
# last -1 reboot
# last -1 shutdown
Getting swap file system usage
# swapinfo -k
Finding out who is logged in and what they are doing
Following all commands can be used. The users command displays the list of all logged in users only on FreeBSD box:# w
# who
# users
Find out when user was last logged in – You can use last command as follows:# last user-name
For example, find out when was user named ‘vivek’ last logged, enter:# last vivek
Say hello to pciconf
Want to find info about the PCI bus and devices on FreeBSD? Try:pciconf -lv
Sample outputs:
ahci0@pci0:4:0:0: class=0x010601 card=0x91721849 chip=0x91721b4b rev=0x11 hdr=0x00 vendor = 'Marvell Technology Group Ltd.' device = '88SE9172 SATA 6Gb/s Controller' class = mass storage subclass = SATA pcib6@pci0:5:0:0: class=0x060400 card=0x11501849 chip=0x11501a03 rev=0x02 hdr=0x01 vendor = 'ASPEED Technology, Inc.' device = 'AST1150 PCI-to-PCI Bridge' class = bridge subclass = PCI-PCI vgapci0@pci0:6:0:0: class=0x030000 card=0x20001849 chip=0x20001a03 rev=0x21 hdr=0x00 vendor = 'ASPEED Technology, Inc.' device = 'ASPEED Graphics Family' class = display subclass = VGA igb0@pci0:7:0:0: class=0x020000 card=0x15331849 chip=0x15338086 rev=0x03 hdr=0x00 vendor = 'Intel Corporation' device = 'I210 Gigabit Network Connection' class = network subclass = ethernet igb1@pci0:8:0:0: class=0x020000 card=0x15331849 chip=0x15338086 rev=0x03 hdr=0x00 vendor = 'Intel Corporation' device = 'I210 Gigabit Network Connection' class = network subclass = ethernet ahci1@pci0:9:0:0: class=0x010601 card=0x92301849 chip=0x92301b4b rev=0x11 hdr=0x00 vendor = 'Marvell Technology Group Ltd.' device = '88SE9230 PCIe SATA 6Gb/s Controller' class = mass storage subclass = SATA |
dmidecode command
FreeBSD users can install the dmidecode tool using the pkg command:# pkg install dmidecode
Sample outputs:
Updating FreeBSD repository catalogue... FreeBSD repository is up to date. All repositories are up to date. The following 1 package(s) will be affected (of 0 checked): New packages to be INSTALLED: dmidecode: 3.2 Number of packages to be installed: 1 62 KiB to be downloaded. Proceed with this action? [y/N]: y [1/1] Fetching dmidecode-3.2.txz: 100% 62 KiB 63.4kB/s 00:01 Checking integrity... done (0 conflicting) [1/1] Installing dmidecode-3.2... [1/1] Extracting dmidecode-3.2: 100% |
Simply run it as follows:# dmidecode
# dmidecode -t processor
# dmidecode -t memory
# dmidecode -t bios
# dmidecode -t 0 ## code for bios (see table below) ##
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | BIOS |
| 1 | System |
| 2 | Baseboard |
| 3 | Chassis |
| 4 | Processor |
| 5 | Memory Controller |
| 6 | Memory Module |
| 7 | Cache |
| 8 | Port Connector |
| 9 | System Slots |
| 10 | On Board Devices |
| 11 | OEM Strings |
| 12 | System Configuration Options |
| 13 | BIOS Language |
| 14 | Group Associations |
| 15 | System Event Log |
| 16 | Physical Memory Array |
| 17 | Memory Device |
| 18 | 32-bit Memory Error |
| 19 | Memory Array Mapped Address |
| 20 | Memory Device Mapped Address |
| 21 | Built-in Pointing Device |
| 22 | Portable Battery |
| 23 | System Reset |
| 24 | Hardware Security |
| 25 | System Power Controls |
| 26 | Voltage Probe |
| 27 | Cooling Device |
| 28 | Temperature Probe |
| 29 | Electrical Current Probe |
| 30 | Out-of-band Remote Access |
| 31 | Boot Integrity Services |
| 32 | System Boot |
| 33 | 64-bit Memory Error |
| 34 | Management Device |
| 35 | Management Device Component |
| 36 | Management Device Threshold Data |
| 37 | Memory Channel |
| 38 | IPMI Device |
| 39 | Power Supply |
| 40 | Additional Information |
| 41 | Onboard Devices Extended Information |
| 42 | Management Controller Host Interface |
Conclusion
This page showed you various command-line tools to gather information about hardware, PCI devices, CPU, RAM, and much more on a FreeBSD based system. See FreeBSD getsysinfo.bash script. It is use to find general FreeBSD system information such as, hostname, OS version, Kernel version, Processor/CPU, Total RAM, System load, network interface, total logged in users, Hard disks, Runlevel etc. Make sure your read the detailed installation instruction.