
I would like to see detailed information on the history of yum transactions such as updates, deleted packages, and other information. How do I see history of yum commands on a CentOS Linux/ RHEL 6.x or 7.x based server? How do I undo or redo or rollback packages using yum command?
The yum command has history option on the latest version of CentOS / RHEL v6.x+. To database are normally found in /var/lib/yum/history/ directory. The history option was added at the the end of 2009 (or thereabouts) to yum command. The history command allows an admin to access detailed information on the history of yum transactions that have been run on a system. You can see what has happened in past transactions (assuming the history_record config. option is set). You can use various command line options to view what happened, undo/redo/rollback to act on that information and start a new history file. This page shows how to use yum history command to find out information about installed, updated, and removed packages.
Prerequisite: Find yum command version on a CentOS/RHEL
You need yum version 3.2.xx or CentOS/RHEL 6.x. Verify this with the following command:# yum info yum | grep --color Version
Sample outputs from CentOS v6.5:
Version : 3.2.29
Here is output from the CentOS Linux box:
CentOS / RHEL See Detailed History Of yum commands
The yum history command allows sysadmin to see information about all Yum command transactions including:
- The dates and times they occurred.
- The number of packages affected.
- Whether transactions succeeded or were aborted.
- If the RPM database was changed between transactions.
- Undo or redo certain transactions.
yum history command syntax
The basic syntax is:
yum history yum history command #ID yum history [options] history [info|list|packages-list|summary|addon-info|redo|undo|rollback|new] |
Examples of yum history command to list package updates
First, verify that history has been configured for yum command.# ls -l /var/lib/yum/history/
Sample outputs:
total 1036 drwxr-xr-x. 30 root root 4096 Dec 9 11:40 2012-11-08 -rw-------. 1 root root 1050624 Dec 9 11:40 history-2012-11-08.sqlite
List history with “yum history”
Type the following command:# yum history
OR# yum history list
Sample outputs:
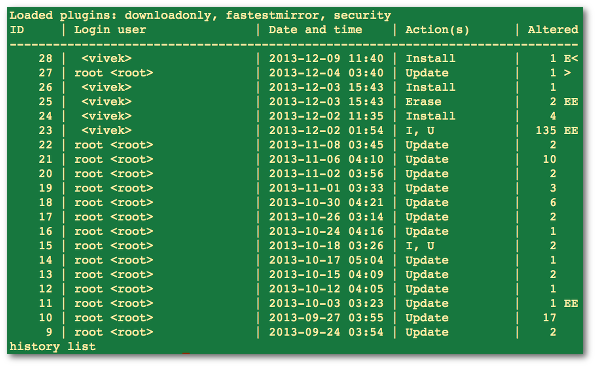
Where,
- ID – Transaction number.
- Login user – The name of the user whose login session was used to initiate a yum.
- Date and time – The date and time when a transaction was issued by yum.
- Action(s) – A list of actions that were performed during a transaction as follows:
- D or Downgrade – Package has been downgraded to an older version.
- E or Erase – Package has been removed.
- I or Install – New package has been installed.
- O or Obsoleting – Package has been marked as obsolete.
- R or Reinstall – Package has been reinstalled.
- U or Update – Package has been updated to a newer version.
- Altered – The number of packages that were affected by a yum, as follows:
- *lt; – Before the transaction finished, the rpmdb database was changed outside yum.
- > – After the transaction finished, the rpmdb database was changed outside yum.
- * – The transaction failed to finish.
- # – The transaction finished successfully, but yum returned a non-zero exit code.
- E – The transaction finished successfully, but an error or a warning was displayed.
- P – The transaction finished successfully, but problems already existed in the rpmdb database.
- s – The transaction finished successfully, but the –skip-broken command line option was used and certain packages were skipped.
To see all transactions, pass the add option as follows:# yum history list all
You can list only one transactions or transactions in a given range:# yum history list 7
# yum history list 1..3
Sample outputs:
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security ID | Login user | Date and time | Action(s) | Altered ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3 | 106300 | 2013-08-12 15:14 | Update | 1 2 | 88177 | 2012-11-09 14:24 | Install | 2 1 | System <unset> | 2012-11-08 19:19 | Install | 380 history list |
How to see listing kernel package operations done with the yum command
Run the following two commands to find when was the last time Linux kernel package was installed or updated:# yum history list kernel
### get info about ID no. 112 ###
# yum history info 112
List summary of all all past transactions
The syntax is:# yum history summary
# yum history summary 3
# yum history summary 1..3
Sample outputs:
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security Login user | Time | Action(s) | Altered ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- <vivek> | Last day | Install | 1 <vivek> | Last week | E, I | 3 root <root> | Last week | Update | 1 <vivek> | Last 2 weeks | I, U | 139 <vivek> | Last 3 months | Update | 1 root <root> | Last 3 months | I, O, U | 284 106300 | Last 6 months | I, U | 6 88177 | Over a year ago | Install | 2 System <unset> | Over a year ago | Install | 380 history summary |
Find out history of a package called nginx
The basic syntax is:# yum history list PackageNameHere
# yum history list nginx
Sample outputs:
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security ID | Login user | Date and time | Action(s) | Altered ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 28 | <vivek> | 2013-12-09 11:40 | Install | 1 EE history list |
You can also see complete history as follows for mysql package including version number, run:# yum history package-list mysql
Sample outputs:
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security ID | Action(s) | Package ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 26 | Install | mysql-5.1.71-1.el6.x86_64 25 | Erase | mysql-5.1.71-1.el6.x86_64 EE 24 | Install | mysql-5.1.71-1.el6.x86_64 history package-list |
Now, use ID #24 to get detailed information on mysql package:# yum history info 24
Sample outputs:
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security Transaction ID : 24 Begin time : Mon Dec 2 11:35:59 2013 Begin rpmdb : 401:d28899f68a6631be573730605bd4825fe661fcce End time : 11:36:03 2013 (4 seconds) End rpmdb : 405:47873bf26c150bf0a26279da5c62d4ae4b1c227d User : <vivek> Return-Code : Success Command Line : install mysql-server mysql Transaction performed with: Installed rpm-4.8.0-37.el6.x86_64 @base Installed yum-3.2.29-40.el6.centos.noarch @base Installed yum-plugin-fastestmirror-1.1.30-14.el6.noarch @base Packages Altered: Install mysql-5.1.71-1.el6.x86_64 @base Install mysql-server-5.1.71-1.el6.x86_64 @base Dep-Install perl-DBD-MySQL-4.013-3.el6.x86_64 @base Dep-Install perl-DBI-1.609-4.el6.x86_64 @base history info |
To find out what additional information is available for a certain transaction:# yum history addon-info id
# yum history addon-info 24
To just get info on last transaction:# yum history addon-info last
How do I undo / revert transactions?
Say, you deleted the nginx package using yum command:# yum erase ngnix
Now, use yum history command to review the transaction history, the yum history command provides means to revert or repeat a selected transaction. To revert (undo) a transaction, type the following at a shell prompt as root:# yum history undo id
To undo nginx erase action, type:# yum history
# yum history package-list nginx
Sample outputs:
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security ID | Action(s) | Package ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29 | Erase | nginx-1.4.4-1.el6.ngx.x86_64 28 | Install | nginx-1.4.4-1.el6.ngx.x86_64 EE history package-list |
To undo use ID # 29:# yum history undo 29
Verify that nginx has been installed again:# yum history package-list nginx
Loaded plugins: downloadonly, fastestmirror, security ID | Action(s) | Package ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 30 | Install | nginx-1.4.4-1.el6.ngx.x86_64 EE 29 | Erase | nginx-1.4.4-1.el6.ngx.x86_64 28 | Install | nginx-1.4.4-1.el6.ngx.x86_64 EE history package-list |
How do I redo / repeat transactions?
To repeat a particular transaction, run:# yum history redo id
The yum history rollback option
The syntax is:# yum history rollback id
The rollback command will undo all transactions up to the point of the specified transaction. For example, if you have 3 transactions, where package A; B and C where installed respectively. Then “yum history undo 1” will try to remove package A, “yum history redo 1” will try to install package A (if it is not still installed), and “yum history rollback 1” will try to remove packages B and C.
The yum new option
As described above, the yum command stores the transaction history in a single SQLite database file in /var/lib/yum/history/ directory. To start new transaction history, run the following command:# yum history new
Verify with the following command:# yum history
I strongly suggest that you read the yum command man page using the man command or this page for more information:$ man yum
