A lot has changed in SEO in the last 18 months. Depending on the type of site you have, this may be a positive or a negative. If you’re an affiliate or a small publishing site, you may have to completely change your model, while anyone running a forum or ecommerce site may have a whole host of new opportunities to rank available to them.
So in the wake of algorithm updates, leaked Google documents, and AI Overviews flooding SERPs and being rolled back, the key question for small businesses is: what still works in SEO in 2024? That’s what we’re going to cover today.
Contents
- Link building
- Content reworks
- Looking like a “real” business
- Forums and user-generated content
- Parasite content
- Programmatic SEO
- Tools and tool sites
- Best of product roundups (on small business sites)
8 SEO tactics that still work in 2024
As with any era of search optimization, the important thing to understand is not how an algorithm impacts everyone so much as how it impacts your site.
Many of the tactics you’ll see people decry “don’t work anymore” actually may work for certain types of sites in certain circumstances (they may have just stopped working for the people who had leveraged them the most and/or advocated for them the loudest).
And as with any era of SEO, there are different rules for different types of sites, and what works for one site won’t work for another.
In this article, I’ll focus on what we’re seeing still working for small businesses with typical small to mid-sized sites. If you have a different type of site, these things may work better or not at all, depending on the tactic, level of authority, and type of site you have.
1. Link building
This should come as no surprise but building quality links to your domain generally—and particularly to pages you want to have rank—still works.
Not all links, of course, are created equal. There are some important caveats that—while they may not have changed much in recent months—are important for businesses to be aware of as they build links or engage with link-building vendors:
- Recently leaked Google documents indicate that the pages you are getting links from actually getting traffic impact the value and perceived quality of the link. In other words: you want links not only from legitimate sites that get traffic, but from individual pages that get real traffic from real people.
- Based on the fact that some sites hit in Google’s recent Helpful Content Update (HCU) appear to have rebounded after cleaning up their link profile, you likely want to be particularly careful about the quality of links pointed to your site, and the linking text.
Of course, all of the usual caveats in terms of ensuring that links are from reputable sites that have links pointed to them apply as well.
? Looking for more ways to drive people to your site? Free guide >> 25 Ways to Increase Traffic to Your Website
2. Content reworks
While a site completely nuked by the HCU may have other issues, if you have a site with older pages where rankings have decayed on those posts, going through a thorough clean-up process to update key pages is still effective.
This is true for a few reasons. Google’s preferred content type (and perceived intent) for a search results page can change over time:
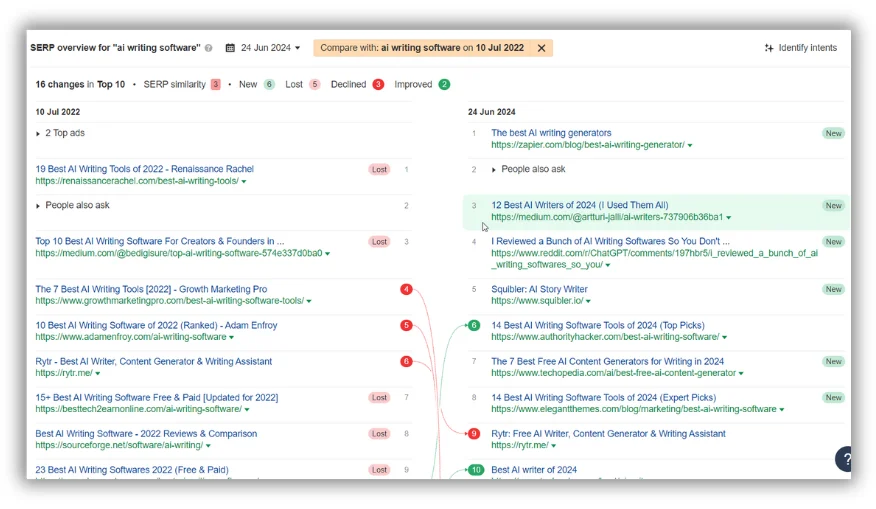

If you had optimized a page for “ai writing software” two years ago, you can see changes here you may want to incorporate as you re-work the page. There may be more diversity in a search results page and the page you have may no longer address what Google’s looking for in the SERP, or the intent may be similar (e.g., a lot of lists still rank in that search result) but the nature of those lists may have changed (e.g., longer or shorter lists, different formatting, etc.)
You need to go back in, look at your content, and make adjustments there. Similarly, you want to audit the internal and external links pointing to key pages (particularly when they’ve lost traffic over time) and make sure that the anchor text you’re using isn’t overly aligned with your target keyword.
3. Looking like a “real” business
You may be thinking “I am a real business! No need to fake it.”
While it’s true you don’t need to “fake” it, it’s also the case that you may need to help signal to Google that you’re a real business and the type of business you are. If you haven’t invested in SEO and/or aren’t a strong brand, your site may have:
- A very low number of external links pointed to it from other sites.
- Limited presence in directories and business data providers (particularly Google’s own Google Business Profile).
- A low number of searches for your brand
What you can control here from an SEO standpoint (beyond link building, which we already mentioned) is making sure you have citations built and that your name, address, and phone number are consistent across data providers. This isn’t limited to businesses with a local presence.
4. Forums and user-generated content
If you’ve searched for anything recently you’ve likely seen Reddit, Quora, and niche forums popping up quite a bit. Depending on your site and your niche, you might consider bolting on a community element (a niche forum or user forum) and/or consider buying a forum in your niche that’s got strong content.
If Goog wants a thing… then just shove that thing at them with both hands ???? pic.twitter.com/yff549ZP1f
— Ian Howells (@ianhowells) June 11, 2024
5. Parasite content
While Google has attempted to crack down on “parasite” content (content hosted on authoritative domains with the aim of ranking for specific phrases) this type of content is still working (for the moment) for many businesses.
Local business owners should be leveraging every parasite imaginable with the current algorithm.
Reddit, Quora, Facebook, LinkedIn Pulse, Medium, etc
Get the page live, index it, build a bunch of tier 2s at it. Until they switch up the algorithm, you want to swarm the first…
— The SEO Guys (@theseoguy_) June 24, 2024
The actual execution of this tactic can vary (i.e. creating lists and including your company, firing “2nd tier” or lower quality links at the page—with the idea being that you don’t need to worry about the link quality since the content is hosted on a third party, high authority domain, etc.). But, even if you’re not going to engage in more aggressive versions of this tactic, it’s worth considering whether you may be able to create content that could live on an authoritative domain to rank well for higher value terms particularly.
? Free guide >> 10 Tangible & Free Ways to Get on the First Page of Google
6. Programmatic SEO
Programmatic SEO is the practice of rolling out programmatically generated pages (now frequently aided/fleshed out with AI-generated content).
I’m seeing big programmatic SEO wins in ecom and digital products.
Example: @benrobertsonio is crushing it on colorbliss.
? pSEO ? display ads
? pSEO ? productsStill the best way to scale IMO. pic.twitter.com/6wgZXkbWF6
— Ian Nuttall (@iannuttall) May 20, 2024
In a previous article, I highlighted some examples of the broad types of pSEO content you may want to consider, such as:
- Geography-based pages (e.g., Housing Costs in {X} with X being New York, Boston, etc.)
- Template Pages (e.g., slideshow templates, excel templates, etc.)
- X vs. Y (e.g., one app vs. another, one product versus another, one type of material vs another, etc.)
- Best X for Y (e.g., best shoes for running, best shoes for lifting, best shoes for basketball, etc.)
In each of these instances, you’d want to have:
- Some sort of data (ideally something proprietary that only you / your company has access to, which leverages your expertise and experience) that applies to the queries in question.
- A strong template with some reusable content and fields to insert the unique queries and data as appropriate.
- Likely some AI-generated content to help build out the content on the pages.
This is a massive “it depends” tactic, as rolling out a lot of largely duplicated, low-value programmatically generated pages for your low-authority small business site can be disastrous and cause you to sink your site rather than help it. If done well with the right data set, the right query space, and on the right site, programmatic SEO does still work.
While a number of mid-authority affiliate and ad-supported sites have been hit by the most recent Helpful Content Update, some of the sites that have survived are tools or calculator sites. These are sites where the purpose of the site is ostensibly that it provides a specific tool or collection of tools.
This is one of the most interesting sites I’ve found.
It gets 3.1 million monthly visitors, and has survived every Google update so far.
— Ian (@keywordian) May 22, 2024
As you might imagine these sites also hang lots of ad-supported and/or affiliate types of content off of the core tool functionality. While your site may be focused on your service or products, this is another area where you could consider building or buying an existing tool site in your niche if you’re a small business.
This boring one-page website makes $18k+ a month.
What it does: calculates accurate daily calorie expenditure
974,000+ visitors a month and going strong.https://t.co/VbCR2lo2r6
(no need to like, repost, or comment “MACRONUTRIENTS” to get the URL ?) pic.twitter.com/l5Nrojp6qV
— Ian Nuttall (@iannuttall) May 24, 2024
Here’s a specific example from the home services niche:
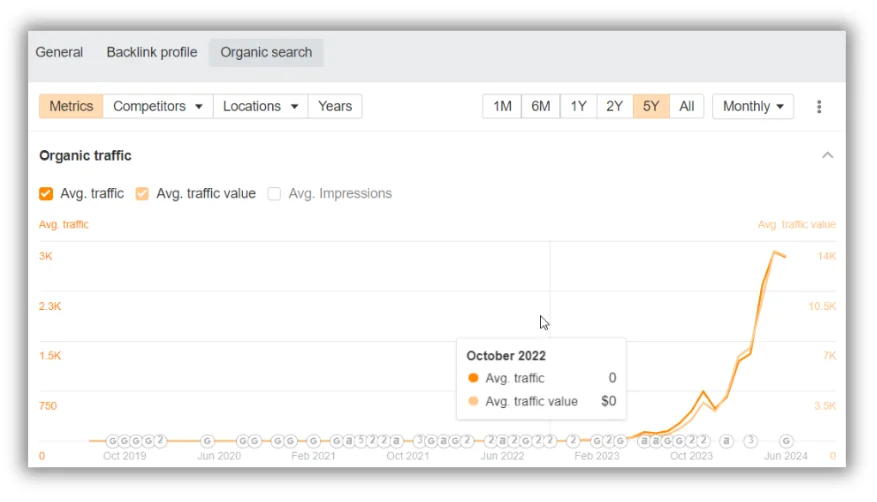

The site in question here is Instant Roofer (I don’t have any affiliation with the site), and they have a roofing cost calculator that uses your address and gives you a cost estimate for replacing your roof:


They then used the same calculator as the primary offer on a number of pages targeting {city/town name} roofing contractors:


Where the pages are also fleshed out with lots of additional information about roof costs in that market (i.e. programmatic SEO content), and even include different vendors:


And this can all be applied at scale:


So if this is working for this site—which is effectively an affiliate site that looks like a tool site—it can certainly work for a number of small business sites.
Calculators specifically can be a great means of building a tool that ranks well for a core term, something that generates lots of quality links and can be spun (with caution!) into additional specific pSEO pages.
? Free guide download >> 135 of the Best Words & Phrases for Marketing with Emotion
8. Best of product roundups (on small business sites)
One of the query spaces that has seen the most shake-up in recent years are product roundups, or best X and best X for Y queries, such as “best brush for Bernedoodles:”


Many of the listings on the left (that ranked in 2022) were informational, ad supported, and affiliate sites. Now, you see Amazon, Reddit, and sites like this one:


All of the products listed in this post are the site’s own products:


If you’re a small business site, you can capture traffic in a few different ways:
- If you’re a services or ecommerce site, you can actually become an affiliate/partner with related products and review and promote products in SERPs where affiliates will no longer be competitive.
- You can create a roundup like the one above to promote your own product or service–either rounding up multiple of your own products/services, or by promoting yourself alongside competitors (they’re not Voldemort, after all).
- Long-form lists of examples, tips, tactics, etc.
Where to start?
As with virtually everything SEO-related: it depends! Certain tactics will fit well with certain sites and certain business goals: look more closely at the possibilities for your site, test, and double down on what works!