
What is Google BERT Update?
Google BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Google BERT is an algorithm that better understands and intuits what users want when they type something into a search engine, like a neural network for the Google search engine that helps power user queries. BERT is a form of open-source intelligence that allows computers to better understand user queries through natural language processing. Google is likely hoping you’ll imagine Bert from Sesame Street.

Google continually makes adjustments so its search functions are more user-friendly, but it can take some time before businesses see just how it will affect their SEO practices. A recent update, Google BERT, stands to affect 10% of all searches.
Ten percent may not sound like much, but when it comes to ranking, it’s huge.
In fact, it’s one of Google’s largest scale updates in the past five years. Arguably one the largest changes since Google launched RankBrain, it’s bound to affect businesses small and large. Learn how BERT will affect search queries and how it may disrupt your business’s content marketing plan.
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
Think of it this way, when you put in a flight number, Google automatically shows you its status. When you put in a business stock number, it will show you how it is performing that day.
Google can effectively predict what you are searching for when you put these concrete figures in, but more vague terms are harder for search engines to process.
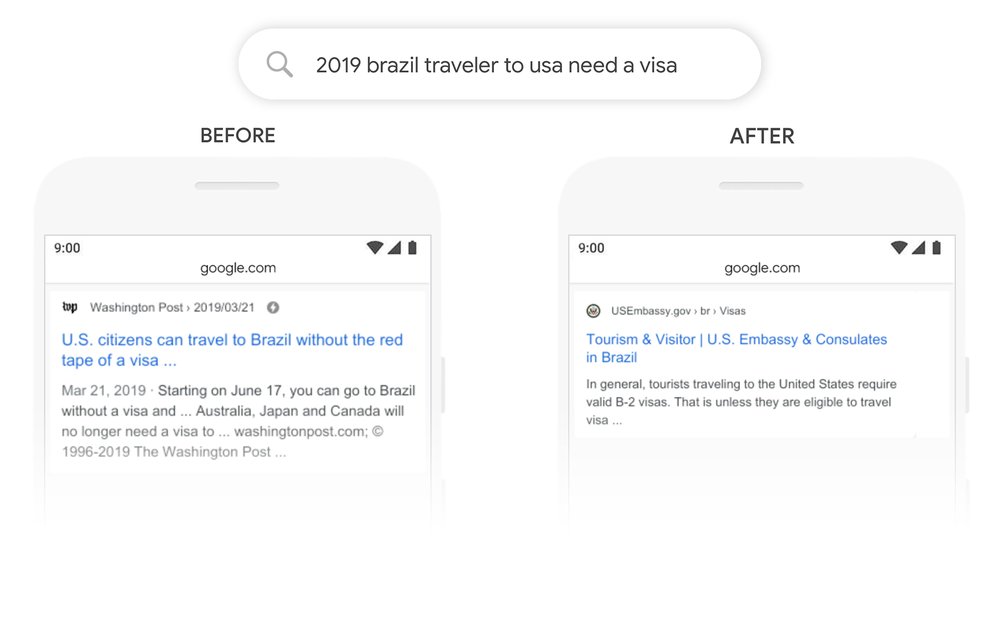
When they released the update, Google gave this search term as an example: “2019 brazil travelers to usa need visa.” Without natural language processing, Google would interpret this as a U.S. citizen needing advice about traveling to Brazil.
With the new BERT update, however, Google should theoretically understand the context of this query and provide more relevant results to a Brazilian seeking information about traveling to the U.S. on a visa.
Here are a couple of other examples of Google BERT in action:
Query: Do estheticians stand a lot at work

Before the BERT update, Google would read the term “stand” as “stand alone.” In other words, the search results were not about physical demand, but the ability to practice in an office by themselves. Now, Google reads this with the intended context.
Query: Can you get medicine for someone pharmacy

Previously, the results would feature tips about getting a prescription filled. Now, they have access to more relevant results about the act of picking up someone else’s prescription.
Google’s BERT update affects more than just search queries – it also makes updates to featured snippets. As the name implies, featured snippets are blocks of content within a page that help the user more readily identify if it contains the information they need. Google BERT also applies its natural language processing algorithm to featured snippets in an effort to garner more relevant results.
For example,
For the featured snippet “parking hill no curb,” Google would place too much weight on the word “curb” instead of the word “no,” which would ultimately affect the search results. Now, users can find more relevant featured snippets that educate on how to park a vehicle on a hill.
How Will BERT Affect My Company SEO?
With any new change that Google launches, there is always some concern for how it will affect SEO practice.
The first thing to understand about BERT is that it does not penalize anyone for their current SEO practices. What’s working for you today should work for you tomorrow. The purpose of BERT is to improve the search engine’s understanding of user queries by using the latest technology available in artificial intelligence.
As such, it will not affect your current website content in the traditional sense. At the same time, any update requires an examination of your current SEO strategy.
Since BERT affects user queries, it’s helpful to know the three main ways that people search for information on Google:
- Informational queries
- Navigational queries
- Transactional queries
These three queries can build on each other. Here’s how that would work.
- Informational: An informational query is one that someone makes when they are seeking an answer to a question. A common example, especially as we near the holidays, might be “how to avoid gaining weight.” Once they perform the search, they will find information about sticking to diet plans over the holidays, portion control, navigating the holiday party scene, and more.
- Navigational: From that search, they may try to hone in more on what they are trying to find, particularly if they are trying to adhere to a certain diet. For example, a navigational query might be “weight watchers diet.”
- Transactional: Once they find the solution they are looking for, they might participate in a transactional query: “weight watchers holiday cookbook” or “weight watchers membership.”
Now that BERT has been active for a couple of months,
SEO experts have noticed that BERT does affect top-of-the-funnel keywords, which are the informational queries. This provides some actionable insight for businesses who want to leverage SEO to get ahead of their competition. To maintain your current rankings or even rise a few places in the SERPs, get more specific with your content.
When you create content for your site (the best way to rank for those informational keywords and queries), SEO best practice tells you to make long-form content – more words mean more chances for Google to find you – or so conventional wisdom says.
You may have heard before that long-form content ranks better on Google, but the key is not to get hung up on a specific word count. Rather, Google algorithms focus on the quality of content, and long-form content gives you more opportunity to do that.
Here are a few key takeaways from the Google BERT update, confirmed by the gurus at Google themselves:
- Focus on creating content that is compelling, useful, and unique. Generic content won’t rank as well as specifics. Following our diet example, if you want to write about “how to avoid weight over the holidays no restrictive diets,” you shouldn’t be writing about Keto or Atkins or anything else similar to fad diets. Instead, focus on all – and we mean all – alternative methods, such as portion control, simple swaps that can cut calories, the timing of food consumption, and more.
- Stop thinking about keyword density. This is an old-school practice. Most SEO experts have been moving away from it in recent years. BERT and the future AI updates will render keywords density obsolete. It will become less and less important as Google’s algorithm better understands the context and what a user is actually looking for.
- Those who want to take full advantage of BERT will focus on creating long, specific, comprehensive content. This jibes best with BERT’s mission – to deliver the best answer to user queries.
- You may notice a drop in traffic after BERT, but think of it less of a punishment and more of an opportunity. If people aren’t finding what they need from your site after getting there from a Google search, they will simply go back and look for it elsewhere, which increases your bounce rate. Now, your current content works to reach users more appropriately. If you’re seeing consistent drops in traffic, revisit your keywords and create long, specific content that speaks to your target user.
Businesses who create meaningfully, unique content shouldn’t worry too much about BERT. The update works to better understand user queries, and those who create comprehensive content with precise keywords will experience improvements in their on-page SEO. By leveraging content and ignoring keyword density, businesses harness the power of BERT to their benefit, boosting traffic and increasing conversions. Expect Google to get smarter with each passing year.
The post What is Google BERT Update? | What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)? first appeared on Web Design & Digital Marketing Tips.