
I like htop output, but it is not installed by default on my Ubuntu cloud server. How do I install htop on Ubuntu Linux 18.04 LTS server?
Htop is a free and open source ncurses-based process viewer for Linux. It is released under GPL license. htop is similar to top command on Linux but allows you to scroll vertically and horizontally. This page explains two different methods to install htop on Ubuntu Linux.
Procedure to install htop on Ubuntu Linux
- Open the terminal application for the local system. For remote system use the ssh command
- Update your Ubuntu system, run: sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
- Install htop on Ubuntu using apt: apt install htop
- To install the latest version of htop on Ubuntu Linux: snap install htop
- Launch htop, type: htop
Let us see all steps and command in details.
Ubuntu Linux Linux install htop
First, update the system using apt command or apt-get command:sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Let us search for htop package, run:apt-cache search htop
Sample outputs:
htop - interactive processes viewer aha - ANSI color to HTML converter libauthen-oath-perl - Perl module for OATH One Time Passwords pftools - build and search protein and DNA generalized profiles
Get information about htop package
Run the following command:apt show htop
Package: htop Version: 2.1.0-3 Priority: optional Section: utils Origin: Ubuntu Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers <ubuntu-devel-discuss@lists.ubuntu.com> Original-Maintainer: Daniel Lange <DLange@debian.org> Bugs: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+filebug Installed-Size: 221 kB Depends: libc6 (>= 2.15), libncursesw5 (>= 6), libtinfo5 (>= 6) Suggests: lsof, strace Homepage: https://hisham.hm/htop/ Task: cloud-image, server, lubuntu-desktop-share, lubuntu-gtk-desktop, lubuntu-desktop, lubuntu-qt-desktop Supported: 5y Download-Size: 80.0 kB APT-Manual-Installed: yes APT-Sources: http://in.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu bionic/main amd64 Packages Description: interactive processes viewer Htop is an ncursed-based process viewer similar to top, but it allows one to scroll the list vertically and horizontally to see all processes and their full command lines. . Tasks related to processes (killing, renicing) can be done without entering their PIDs. |
Install htop using apt or apt-get
Now you know package name. It is time to install the same:sudo apt install htop
ORsudo apt-get install htop
How to install the latest version of htop using snap
Search for htop using the snap command:snap search htop
Sample outputs:
Name Version Publisher Notes Summary htop 2.2.0 maxiberta - Interactive processes viewer |
Next, install it using the snap, run:sudo snap install htop
Sample outputs:
[sudo] password for vivek: htop 2.2.0 from Maximiliano Bertacchini (maxiberta) installed |
How to use htop command
The syntax is:htop
htop [options]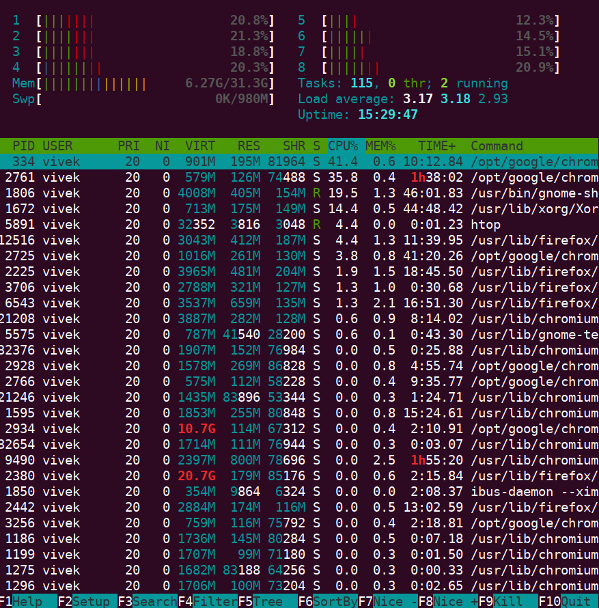
One can use a monochrome color scheme, run:htop -C
htop --no-color
Want to see the tree view by default when running htop? Try:htop -t
htop --tree
Let us see only processes of a given user named vivek:htop -u vivek
htop --user=vivek
htop --user=nginx
Limit and show process for only the given PIDs:htop -p PID
htop -p PID1,PID2
--pid=PID,[,PID,PID...]
htop -p 1342
htop -p 7435,1367
htop command keyboard shortcut keys
Now that you install htop on Ubuntu. It is time to learn keyboard shortcuts. The following commands are supported while in htop session:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Up arrow key | Select (highlight) the previous process in the process list. Scroll the list if necessary. |
| Down arrow key | Select (highlight) the next process in the process list. Scroll the list if necessary. |
| Left arrow key | Scroll the process list left. |
| Right arrow key | Scroll the process list right. |
| PgUp, PgDn | Scroll the process list up or down one window. |
| Home | Scroll to the top of the process list and select the first process. |
| End | Scroll to the bottom of the process list and select the last process. |
| s | Trace process system calls: if strace(1) is installed, pressing this key will attach it to the currently selected process, presenting a live update of system calls issued by the process. |
| l | Display open files for a process: if lsof(1) is installed, pressing this key will display the list of file descriptors opened by the process. |
| u | Show only processes owned by a specified user. |
| M | Sort by memory usage (top compatibility key). |
| P | Sort by processor usage (top compatibility key). |
| T | Sort by time (top compatibility key). |
| F | “Follow” process: if the sort order causes the currently selected process to move in the list, make the selection bar follow it. This is useful for monitoring a process: this way, you can keep a process always visible on screen. When a movement key is used, “follow” loses effect. |
| K | Hide kernel threads: prevent the threads belonging the kernel to be displayed in the process list. (This is a toggle key.) |
| H | Hide user threads: on systems that represent them differently than ordinary processes (such as recent NPTL-based systems), this can hide threads from userspace processes in the process list. (This is a toggle key.) |
| p | Show full paths to running programs, where applicable. (This is a toggle key.) |
| Ctrl-L | Rfresh the screen. |
| F1 | See this help menu. |
| h | Same as above. |
| ? | Again, same as above. |
| F10 | Quit htop |
| q | Exit htop (same as above) |
How to get help about htop
Simply type:htop --help
man htop
Conclusion
This page showed you how to install and use htop on Ubuntu Linux 16.04/18.04 LTS. For more information see htop home page online here.
