
I need to list all open ports in Linux cloud server. How do I check open ports in Linux using the CLI? Can you give me the command to check open ports in Linux operating system?
To troubleshoot server problems and to avoid security issue, one needs to find out open TCP and UDP ports. In this tutorial, you will learn the different Linux commands to check open ports in Linux for auditing and securing the server.
What the hell are a TCP and UDP ports?
A port is nothing but a 16-bit number between 0 to 65535. For example, TCP port number 22 may be forwarded to the OpenSSH server. Therefore, 22 port number is a way to identify the sshd (OpenSSH server) process.
Port numbers
- The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023.
- The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151.
- The Dynamic and Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535.
A registered port is a network port assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and stored in /etc/services file. Use the cat command or grep command/egrep command to view port numbers and service mappings:
cat /etc/services grep -w '80/tcp' /etc/services grep -w '443/tcp' /etc/services egrep -w '22/(tcp|udp)' /etc/services |
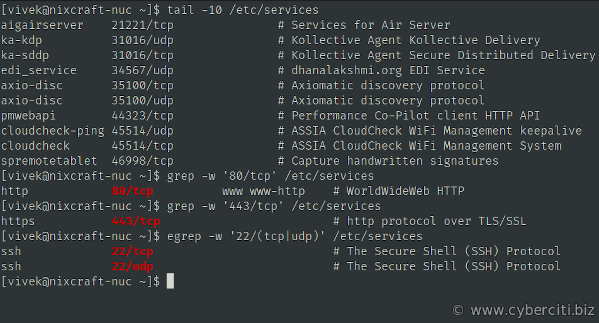
Check open ports in Linux
The procedure to monitor and display open ports in Linux is as follows:
- Open a Linux terminal application
- Use ss command to display all open TCP and UDP ports in Linux.
- Another option is to use the netstat command to list all ports in Linux.
- Apart from ss/netstat one can use the lsof command to list open files and ports on Linux based system.
- Finally, one can use nmap command to check TCP and UDP ports too.
Let us see all commands and examples in details.
Using netstat to list open ports
Type the following netstat commandsudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN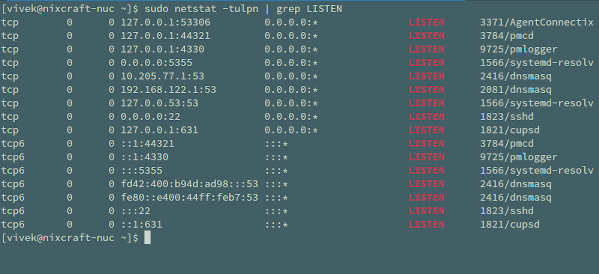
For example, TCP port 631 opened by cupsd process and cupsd only listing on the loopback address (127.0.0.1). Similarly, TCP port 22 opened by sshd process and sshd listing on all IP address for ssh connections:
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State User Inode PID/Program name tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 43385 1821/cupsd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 44064 1823/sshd
Where,
- -t : All TCP ports
- -u : All UDP ports
- -l : Display listening server sockets
- -p : Show the PID and name of the program to which each socket belongs
- -n : Don’t resolve names
- | grep LISTEN : Only display open ports by applying grep command filter.
Use ss to list open ports
The ss command is used to dump socket statistics. It allows showing information similar to netstat. It can display more TCP and state information than other tools. The syntax is:sudo ss -tulpn
Sample outputs:
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port udp UNCONN 0 0 224.0.0.251:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chromium-browse",pid=12893,fd=419)) udp UNCONN 0 0 224.0.0.251:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chromium-browse",pid=12938,fd=395)) udp UNCONN 0 0 224.0.0.251:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chrome",pid=10111,fd=178)) udp UNCONN 0 0 224.0.0.251:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chrome",pid=10111,fd=139)) udp UNCONN 0 0 224.0.0.251:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chrome",pid=10111,fd=48)) udp UNCONN 0 0 224.0.0.251:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chrome",pid=10161,fd=43)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:5353 0.0.0.0:* users:(("avahi-daemon",pid=1590,fd=15)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:5355 0.0.0.0:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=1566,fd=12)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:55204 0.0.0.0:* users:(("avahi-daemon",pid=1590,fd=17)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:49112 0.0.0.0:* users:(("openvpn",pid=18342,fd=8)) udp UNCONN 0 0 10.205.77.1:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=8)) udp UNCONN 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2081,fd=5)) udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.53%lo:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=1566,fd=17)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0%lxdbr0:67 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=4)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0%virbr0:67 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2081,fd=3)) udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:68 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dhclient",pid=18263,fd=7)) udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:* users:(("chronyd",pid=1652,fd=6)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:5353 [::]:* users:(("avahi-daemon",pid=1590,fd=16)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:5355 [::]:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=1566,fd=14)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:60302 [::]:* users:(("avahi-daemon",pid=1590,fd=18)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [fd42:400:b94d:ad98::1]:53 [::]:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=12)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [fe80::e400:44ff:feb7:3233]%lxdbr0:53 [::]:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=10)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::1]:323 [::]:* users:(("chronyd",pid=1652,fd=7)) udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]%lxdbr0:547 [::]:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=6)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:53306 0.0.0.0:* users:(("AgentAntidote.b",pid=6206,fd=16),("AgentAntidote",pid=6164,fd=16),("AgentConnectix.",pid=3371,fd=16)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 127.0.0.1:44321 0.0.0.0:* users:(("pmcd",pid=3784,fd=0)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 127.0.0.1:4330 0.0.0.0:* users:(("pmlogger",pid=9725,fd=9)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:5355 0.0.0.0:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=1566,fd=13)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 10.205.77.1:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=9)) tcp LISTEN 0 32 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2081,fd=6)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.53%lo:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=1566,fd=18)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* users:(("sshd",pid=1823,fd=5)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* users:(("cupsd",pid=1821,fd=10)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:44321 [::]:* users:(("pmcd",pid=3784,fd=3)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:4330 [::]:* users:(("pmlogger",pid=9725,fd=10)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:5355 [::]:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=1566,fd=15)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 [fd42:400:b94d:ad98::1]:53 [::]:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=13)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 [fe80::e400:44ff:feb7:3233]%lxdbr0:53 [::]:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=2416,fd=11)) tcp LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* users:(("sshd",pid=1823,fd=7)) tcp LISTEN 0 5 [::1]:631 [::]:* users:(("cupsd",pid=1821,fd=9)) |
Listening ports and applications using lsof command
Let us run the following to check open TCP and UDP ports using the lsof command:sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
Where,
- -i : Look for listing ports
- -P : Inhibits the conversion of port numbers to port names for network files. Inhibiting the conversion may make lsof run a little faster. It is also useful when port name lookup is not working properly.
- -n : Do not use DNS name
- | grep LISTEN : Again only show ports in LISTEN state using the grep command as filter.
nmap command
In addition, to above commands one can use the nmap command which is an open source tool for network exploration and security auditing. We are going to use nmap to find and list open ports in Linux:$ sudo nmap -sT -O localhost
$ sudo nmap -sU -O 192.168.2.254 ##[ list open UDP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sT -O 127.0.0.1 ##[ list open TCP ports ]##
$ sudo nmap -sTU -O 192.168.2.24
Sample outputs:
Starting Nmap 7.70 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2019-07-22 23:49 IST Nmap scan report for localhost (127.0.0.1) Host is up (0.00024s latency). Other addresses for localhost (not scanned): ::1 Not shown: 998 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE 22/tcp open ssh 631/tcp open ipp Device type: general purpose Running: Linux 2.6.X OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:2.6.32 OS details: Linux 2.6.32 Network Distance: 0 hops OS detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 2.31 seconds |
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding out open ports is one of the most fundamental duties of a Linux system administrator for security reasons. Therefore, close down all unwanted ports and configure firewall such as UFW and FirewallD to open or block ports as per your requirements. After reading this tutorial, you should have a good understanding of how to check for open ports in Linux. See IANA’s offical list of TCP, UDP and other ports here for more information.